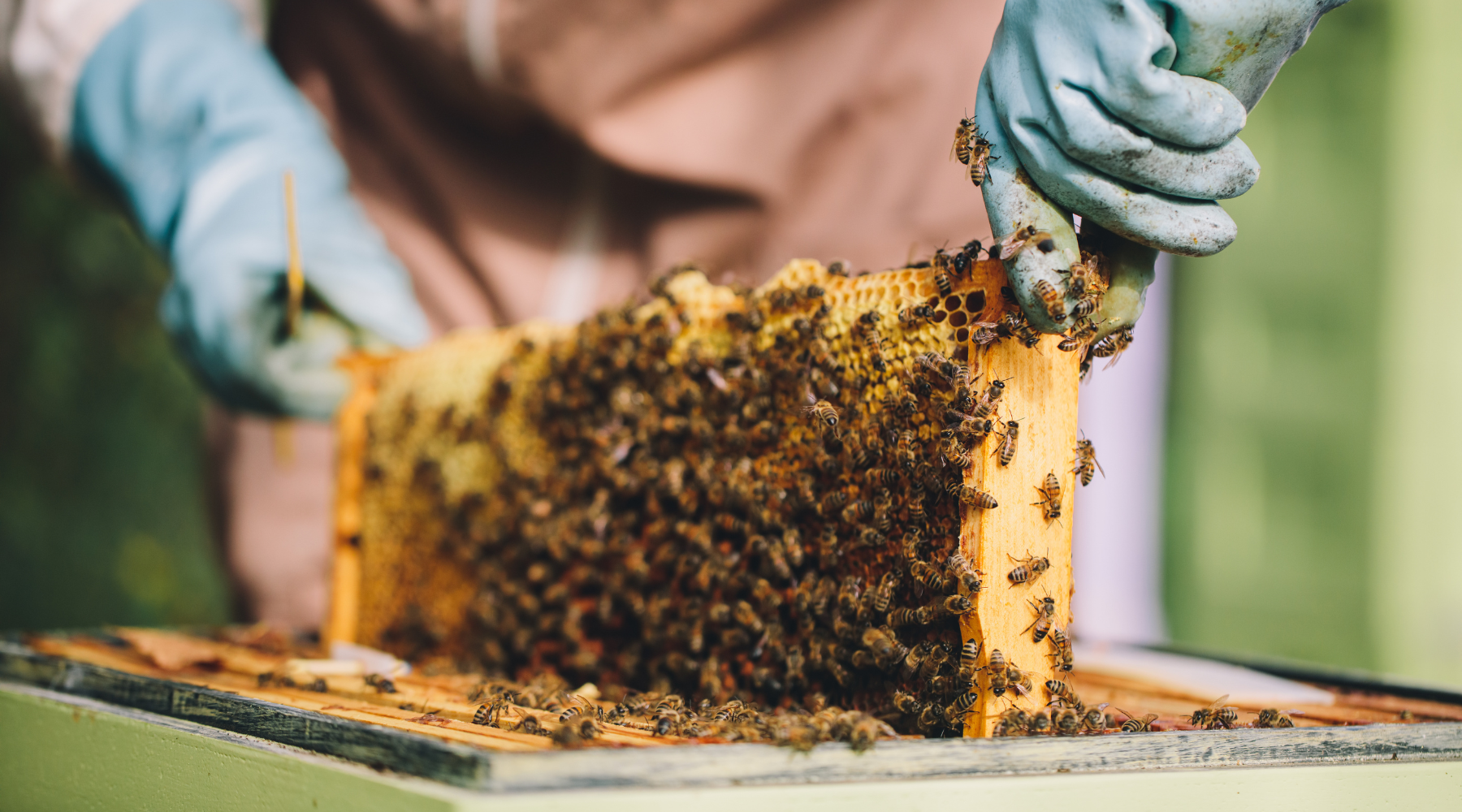
Mānuka honey, celebrated for its unique benefits and rich flavour, has captured global interest. Have you ever wondered about the process behind its production? At the heart of every hive is the queen bee, playing a crucial role in creating mānuka honey. The queen bee's main job is to lay eggs, ensuring a steady supply of worker bees to collect nectar from mānuka flowers. These flowers bloom for only a few weeks each year, making it essential for the hive to be at peak efficiency.
In addition to laying eggs, the queen bee releases pheromones to regulate hive activities, keeping the colony productive. These signals help maintain order and motivate worker bees to perform their tasks. Without the queen bee's work and the well-coordinated efforts of her colony, the production of Primal By Nature mānuka honey wouldn't be possible. Understanding her role gives us a deeper appreciation for this extraordinary honey.
Meet the Queen Bee
The queen bee is the cornerstone of the hive. Unlike other bees, there's only one queen per hive. Her main job is to lay eggs, ensuring the colony's growth and survival. While this might sound simple, her role is far more complex and vital to the production of mānuka honey.
The Life of the Queen Bee
The journey of a queen bee starts with her being chosen from birth. Worker bees select a few larvae and feed them a special substance called "royal jelly." This exclusive diet triggers the development of a queen bee. Once she matures, she embarks on a mating flight, where she mates with multiple drones (male bees) to collect enough sperm to fertilise eggs for the rest of her life.
Laying the Foundation for Manuka Honey
The queen bee's primary function is to lay eggs. She can lay up to 2,000 eggs per day during peak season. These eggs hatch into larvae, which then develop into worker bees, drones, or new queens. The continuous laying of eggs ensures a steady supply of worker bees to gather nectar from Mānuka flowers, which is essential for honey production.
The Hive’s Manuka Honey Workforce
Worker bees, all daughters of the queen, are the hive's labour force. They perform various tasks, including foraging for nectar, which they turn into honey. Mānuka honey production is particularly demanding because Mānuka flowers only bloom for a few weeks a year. During this period, worker bees must be at their most productive.
The Queen’s Influence on Pure Manuka Honey
The queen bee has a unique way of communicating with her colony. She releases pheromones, which are chemical signals that regulate the hive's behaviour and activities. These pheromones ensure that the workers remain loyal and motivated, maintain the hive’s structure, and continue with their roles efficiently. This harmonious operation is critical during the Mānuka flowering season.
Manuka Flowers and Nectar
Mānuka trees are native to New Zealand and known for their small, white or pink flowers. These flowers produce nectar that bees collect and convert into Mānuka honey. The timing of nectar collection is crucial because the Mānuka flowers bloom for a short period. The queen bee’s ability to maintain a strong, active workforce directly impacts the efficiency of nectar collection.
From Nectar to Manuka Honey
Once the worker bees collect the nectar, they return to the hive and pass it to other worker bees. Through a process called trophallaxis, the nectar is passed from bee to bee, gradually reducing its water content. The bees then deposit the nectar into honeycomb cells, where they fan it with their wings to evaporate more water, eventually turning it into thick, rich honey.
The Importance of a Strong Hive
A strong, healthy hive is essential for efficient honey production. The queen bee’s prolific egg-laying ensures a robust population of worker bees. Without enough workers, the hive wouldn’t be able to gather enough nectar or produce sufficient honey, especially within the short mānuka flowering window.
The Unique Qualities of Manuka Honey
Mānuka honey is prized for its distinctive taste and renowned properties. It contains high levels of methylglyoxal (MGO), which gives it unique properties. The quality and potency of mānuka honey depend on various factors, including the health and efficiency of the bee colony, directly influenced by the queen bee.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors also play a significant role in mānuka honey production. Weather conditions, the availability of mānuka flowers, and the overall health of the environment affect nectar availability. A well-maintained hive, led by a strong queen, can better adapt to these conditions and maximise honey production.
Beekeepers’ Role
Beekeepers play a crucial role in supporting the queen bee and her colony. They ensure the hive is healthy, monitor the queen’s performance, and make necessary interventions, such as replacing an aging queen. By doing so, they help maintain a strong workforce capable of producing high-quality mānuka honey.
Challenges in Manuka Honey Production
Producing mānuka honey isn’t without challenges. The short blooming period of mānuka flowers means there’s a limited time to collect nectar. Additionally, environmental threats like pests, diseases, and climate change can impact hive health and productivity. A strong queen bee and a well-managed hive are vital to overcoming these challenges.
Sustainability and Manuka Honey
Sustainability is a key concern in honey production. Beekeepers and companies like Primal By Nature are committed to environmentally friendly practices that protect bee populations and their natural habitats. These practices include planting more mānuka trees, using organic farming methods, and avoiding harmful chemicals.
The Future of Mānuka Honey with Primal By Nature
The future of mānuka honey looks promising, with increasing global demand for its health benefits. At Primal By Nature, we are committed to the best practices and recognise the pivotal role of the queen bee in ensuring that this precious honey remains available for generations to come.
By supporting environmentally friendly beekeeping and honouring the incredible contributions of the queen bee and her colony, we aim to preserve the quality and availability of mānuka honey for the future.
How the Queen Bee Helps Produce Manuka Honey
The queen bee’s role in mānuka honey production is undeniably vital. Her ability to maintain a strong, efficient hive directly impacts the quality and quantity of honey produced. From laying thousands of eggs to communicating with her colony, the queen bee is at the heart of this intricate process.
By understanding her role, we gain a deeper appreciation for the hard work and dedication that goes into every jar of genuine mānuka honey.
At Primal By Nature, we’re proud to support environmentally friendly beekeeping practices that honour the incredible contributions of the queen bee and her colony and ensure the continued production of this extraordinary honey.